This tutorial describes the setup of a development workstation
Required Hardware
- Sawyer Robot & Developer Workstation
Workstation Requirements
- A development workstation capable of running Ubuntu 16.04 LTS and ROS Kinetic (or Ubuntu 14.04 LTS and ROS Indigo), with the following minimum specifications:
- Intel i5 or above
- 4GB Memory or above
- At least 7 GB of free disk space
- Ethernet port
- If any visualization (RViz) or simulation (Gazebo) is required for your application, a dedicated NVidia graphics card with proprietary NVidia drivers is recommended
Install Ubuntu
Follow the standard Ubuntu Installation Instructions for 16.04 (Desktop):
- Download the Installer Image file, by picking the "Desktop CD" image appropriate for your machine:
- Create an Ubuntu LiveUSB installer by burning the installer image onto a USB stick.
- Follow the Ubuntu Installation Instructions
Follow the standard Ubuntu Installation Instructions for 14.04 (Desktop):
- Download the Installer Image file, by picking the "Desktop CD" image appropriate for your machine:
- Create an Ubuntu LiveUSB installer by burning the installer image onto a USB stick.
- Follow the Ubuntu Installation Instructions
Open Terminal App
Search your computer for the Terminal package, and open it:
The rest of the workstation setup tutorial will take place in by typing commands in this terminal prompt.
Install ROS
Configure Ubuntu repositories
Configure your Ubuntu repositories to allow "restricted," "universe," and "multiverse." You can follow the Ubuntu guide for instructions on doing this.
Likely, they are already configured properly, and you only need to confirm the configuration.
Setup your sources.list
$ sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://packages.ros.org/ros/ubuntu xenial main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ros-latest.list'
Setup your keys
$ sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://ha.pool.sks-keyservers.net:80 --recv-key 421C365BD9FF1F717815A3895523BAEEB01FA116
Update to Latest Software Lists
$ sudo apt-get update
Install ROS Kinetic Desktop Full
$ sudo apt-get install ros-kinetic-desktop-full
Initialize rosdep
rosdep enables you to easily install system dependencies for source you want to compile and is required to run some core components in ROS.
$ sudo rosdep init
$ rosdep update
Install rosinstall
$ sudo apt-get install python-rosinstall
Configure Ubuntu repositories
Configure your Ubuntu repositories to allow "restricted," "universe," and "multiverse." You can follow the Ubuntu guide for instructions on doing this.
Likely, they are already configured properly, and you only need to confirm the configuration.
Setup your sources.list
$ sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://packages.ros.org/ros/ubuntu trusty main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ros-latest.list'
Setup your keys
$ sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://ha.pool.sks-keyservers.net:80 --recv-key 421C365BD9FF1F717815A3895523BAEEB01FA116
Update to Latest Software Lists
$ sudo apt-get update
Install ROS Indigo Desktop Full
$ sudo apt-get install ros-indigo-desktop-full
NOTE: You may get a prompt about 'hddtemp' during the installation. You can safely answer 'No'.
Initialize rosdep
rosdep enables you to easily install system dependencies for source you want to compile and is required to run some core components in ROS.
$ sudo rosdep init
$ rosdep update
Install rosinstall
$ sudo apt-get install python-rosinstall
Create Development Workspace
Create ROS Workspace
$ mkdir -p ~/ros_ws/src
# ros_ws (short for ROS Workspace)
Source ROS and Build
ROS Kinetic
Source ROS Setup
$ source /opt/ros/kinetic/setup.bash
Build
$ cd ~/ros_ws
$ catkin_make
Create ROS Workspace
$ mkdir -p ~/ros_ws/src
# ros_ws (short for ROS Workspace)
Source ROS and Build
ROS Indigo (Supported)
Source ROS Setup
$ source /opt/ros/indigo/setup.bash
Build
$ cd ~/ros_ws
$ catkin_make
Install Intera SDK Dependencies
Install SDK Dependencies
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install git-core python-argparse python-wstool python-vcstools python-rosdep ros-kinetic-control-msgs ros-kinetic-joystick-drivers ros-kinetic-xacro ros-kinetic-tf2-ros ros-kinetic-rviz ros-kinetic-cv-bridge ros-kinetic-actionlib ros-kinetic-actionlib-msgs ros-kinetic-dynamic-reconfigure ros-kinetic-trajectory-msgs ros-kinetic-rospy-message-converter
Install SDK Dependencies
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install git-core python-argparse python-wstool python-vcstools python-rosdep ros-indigo-control-msgs ros-indigo-joystick-drivers ros-indigo-xacro ros-indigo-tf2-ros ros-indigo-rviz ros-indigo-cv-bridge ros-indigo-actionlib ros-indigo-actionlib-msgs ros-indigo-dynamic-reconfigure ros-indigo-trajectory-msgs ros-indigo-rospy-message-converter
Install Intera Robot SDK
Download the SDK on your Workstation
Checkout all required Github Repositories into your ROS workspace source directory: Use git clone or download the packages directly from Github:
$ cd ~/ros_ws/src
$ wstool init .
$ git clone https://github.com/RethinkRobotics/sawyer_robot.git
$ wstool merge sawyer_robot/sawyer_robot.rosinstall
$ wstool update
Source ROS Setup
To use ROS Kinetic to use RSDK, use command below:
# ROS Kinetic
$ source /opt/ros/kinetic/setup.bash
Build
$ cd ~/ros_ws
$ catkin_make
Download the SDK on your Workstation
Checkout all required Github Repositories into your ROS workspace source directory: Use git clone or download the packages directly from Github:
$ cd ~/ros_ws/src
$ wstool init .
$ git clone https://github.com/RethinkRobotics/sawyer_robot.git
$ wstool merge sawyer_robot/sawyer_robot.rosinstall
$ wstool update
Source ROS Setup
To use ROS Kinetic to use RSDK, use command below:
# ROS Kinetic
$ source /opt/ros/indigo/setup.bash
Build
$ cd ~/ros_ws
$ catkin_make
Configure Robot Communication/ROS Workspace
This step describes the configuration and setup of your ROS environment. This section assumes you have linked your workstation to the robot via Ethernet.
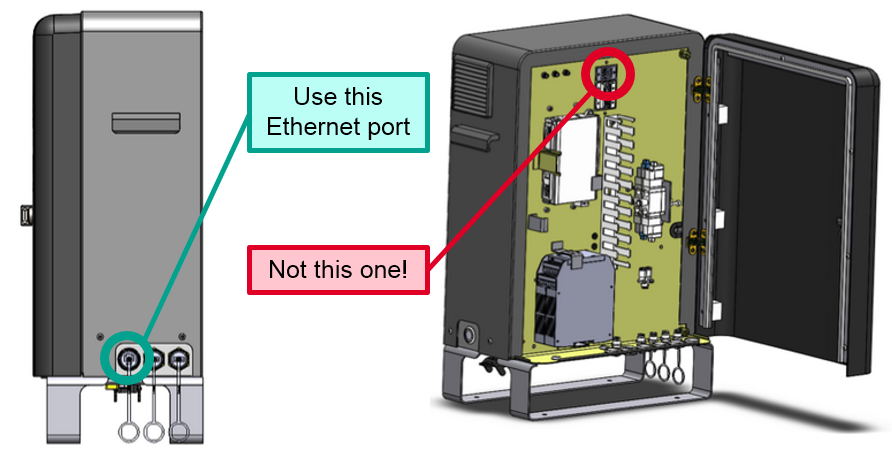
Important Note: Connect to the robot via the ethernet port on the outside of the Controller. Connecting to the ethernet port inside the Controller door will not work (this is a diagnostic port that is only accessible by Rethink Employees).
See Network Setup for recommended network configurations.
intera.sh ROS Environment Setup
The intera.sh script is a convenience script which allows for intuitive modification of the core ROS environment components. This user edited script will allow for the quickest and easiest ROS setup.
Further information and a detailed description is available on the SDK_Shell page.
Copy the intera.sh script
The intera.sh file already exists in intera_sdk repo, copy the file into your ros workspace.
$ cp ~/ros_ws/src/intera_sdk/intera.sh ~/ros_ws
Customize the intera.sh script
Please edit the intera.sh shell script making the necessary modifications to describe your development PC.
Using your favorite editor (gedit used for example)
$ cd ~/ros_ws
$ gedit intera.sh
Edit the 'robot_hostname' field
Your robot's hostname is defaulted as the Controller's Serial Number and NOT the Robot's Serial Number. The serial number can be located on the back of the robot's controller box. Unless you intend to modify the default Networking configuration, leave the ".local" suffix on the end of the Controller's Serial Number in the robot_hostname.local field.
Edit the 'your_ip' field
Modify where 'your_ip' is either your computer's hostname or the IP address of your PC. We advise against using WiFi connections between your robot and workstation.
your_ip="192.168.XXX.XXX"
Useful command for identifying your IP address:
$ ifconfig
# Result will be contained in the 'inet addr' field (Ubuntu).
Alternatively, you may choose to use the hostname of your development PC rather than the PC's IP address. For instructions, press Expand on the right.
You may edit the 'your_hostname' field (only if not using 'your_ip'):
your_hostname="my_computer.local
Important: This hostname must be resolvable to Sawyer. To test if your hostname is resolvable to Sawyer, please visit the development PC Hostname Validation page.
Important: Only set either ROS_IP *OR* ROS_HOSTNAME.
Setting of both ROS_IP and ROS_HOSTNAME will result in ROS_HOSTNAME taking priority, resulting in confusing environment setups. Comment out the unused method using the '#' as leading character.
Verify 'ros_version' field
Verify that the the 'ros_version' field matches the ROS version you are running:
This field will default to "indigo". To use another ROS version, update:
ros_version="kinetic"
ros_version="indigo"
Save and Close intera.sh script
Please save and close the intera.sh script.
Initialize your SDK environment
From this point forward, your ROS environment setup should be as simple as sourcing the intera.sh script from the root of your Catkin workspace:
$ cd ~/ros_ws
$ ./intera.sh
Verify Environment
A useful command for viewing and validating your ROS environment setup is:
$ env | grep ROS
The important fields at this point:
ROS_MASTER_URI - This should now contain your robot's hostname.
ROS_IP - This should contain your workstation's IP address.
or
ROS_HOSTNAME - If not using the workstation's IP address, the ROS_HOSTNAME field should contain your PC's hostname. Otherwise, this field should not be available.
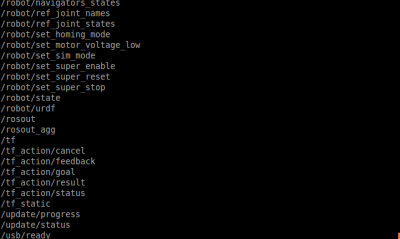
Try to get rostopic list from robot by typing following command:
$ rostopic list
You can see the rostopic list from the command line output similar as following:
Setup Rviz
We can also setup Rviz to view robot model, start Rviz from a properly initialized environment using:
$ rosrun rviz rviz
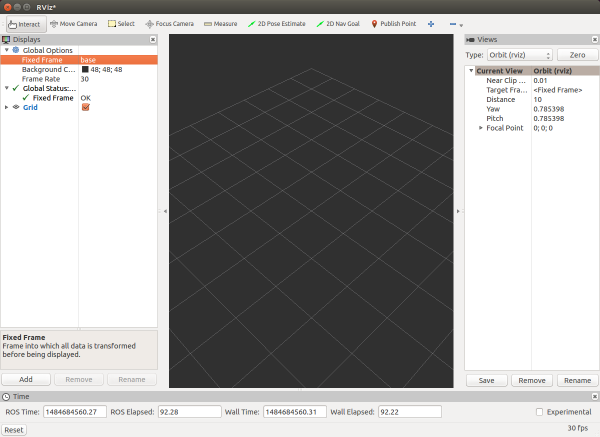
Set the Fixed Frame as /base
Info: The ‘Fixed Frame’ provides a static, base reference for your visualization. Any sensor data that comes in to rviz will be transformed into that reference frame so it can be properly displayed in the virtual world.
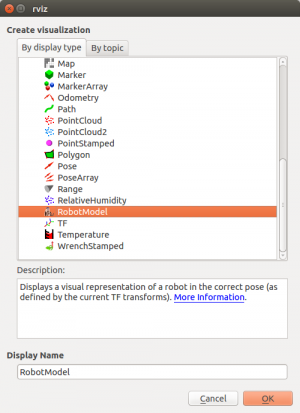
Add robot model into Rviz by clicking add button, then select robot model in the list, press OK to add.
Now you can visualize your robot on Rivz! Next : Hello Robot